Financial institutions are adopting digital tools within the banking industry at a rapid pace, which is driving demand for trustworthy data protection systems and robust cyber security precautions.
There is no sign that the level of cyber risk in the banking sector is likely to decrease. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs will reach 10.5 trillion U.S. dollars annually by 2025. No matter how frightening these statistics may seem, banking organizations have a chance to avoid financial and reputational losses. How, you may ask? By implementing reliable cyber security measures.
Dealing with challenges
In the dynamic environment of the financial sphere, challenges are inescapable, ranging from cyber attacks and legislative requirements to evolving customer cyber security demands. The key skill here is the adaptability to high-speed digital transformation and active resistance to cybersecurity threats.
Latest Cybersecurity Threats in Banking

According to Statista, in 2023, the average cost of a data leak across all sectors in the United States reached 9.48 million U.S. dollars, the highest position worldwide. An average data breach in the financial sector costs 5.9 million U.S. dollars, ranking the financial industry second based on the average cost of data breaches worldwide.

Financial institutions risk losing millions of dollars and reputation in case cyber attackers make use of system vulnerabilities. Let’s take a closer look at the latest cyber threats.
Phishing attacks
Phishing attacks are dominant threats in banking industry cybersecurity, as the financial sector is the field most targeted by phishing scams. In 2023, over 23 percent of phishing attacks worldwide targeted financial institutions. Phishers pose as legitimate banks or financial institutions. They target unaware people by sending fake forms, misleading emails, or messages containing malign links aimed to obtain sensitive information. The miscreants penetrate the network of a financial institution and can carry out a more significant attack aimed at data theft.
One of the common phishing tactics is creating a sense of urgency or panic. The attackers state that the account of a receiver has faced suspicious activity, or their information is required to be updated right away. The aim is to make users act without thinking critically.

Malware
Malware, or malicious software, intends to obtain sensitive financial information, such as account numbers or passwords, and violate financial transactions. Malicious software poses a considerable cybersecurity threat in the banking sector due to its ability to implement various methods to break through security measures and infect devices. According to Statista, in 2023, the worldwide number of malware attacks hit 6.06 billion U.S. dollars, including ones in the banking sector.
Trojans and keyloggers
Banking trojans are a type of malware designed to target your online banking information. They act like a digital trojan horse, pretending to be legitimate applications while secretly deceiving you. Trojans imitate the appearance of your bank official login page. They intercept login details and codes within a banking session.
This misleading tactic plunges you in a bogus feeling of security, aiming to deceive you and steal your sensitive personal information. As soon as installed, banking trojans act like information vacuums and absorb your financial data. Trojans often implement the technique of keylogging, which records all the information you type, such as usernames, passwords, and one-time codes.
Ransomware
In 2023, organizations worldwide detected 317.59 million U.S. dollars ransomware attempts, making 72 percent of businesses worldwide affected by ransomware attacks. Ransomware is a type of malware that targets the data of a user or organization, taking it hostage and demanding a ransom charge for its release. In the banking sector, ransomware attacks are especially harmful as they disrupt financial operations and put confidential financial information at risk.
Ransomware can encrypt critical data, such as customer information, financial records, and transaction details. This encryption renders the data unreadable and inaccessible, and locks the bank out of its own data. With critical data locked away, crucial operations like processing transactions, accessing customer accounts, and even internal communications can become impossible.
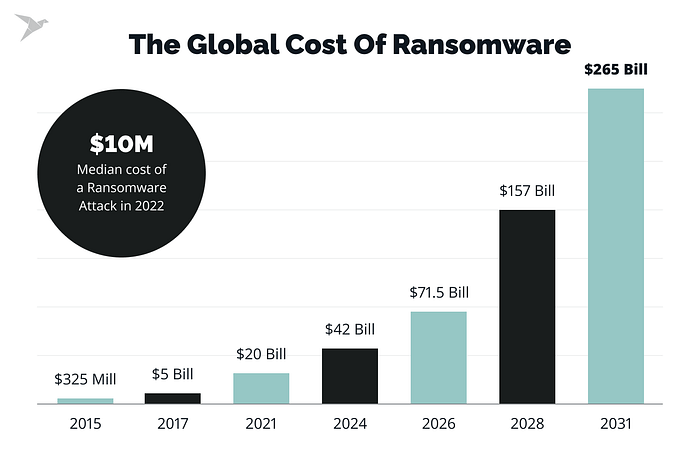
The potential reputational and financial losses put banks under the pressure to pay the ransom to recover bank activity rapidly. According to Cybersecurity Ventures prediction, ransomware will cost its victims around 265 billion U. S. dollars annually by 2031.
Third party risk
Third party integrations boost the efficiency for banking institutions, but they also introduce significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Every third party system a bank connects to creates a new entry point for attackers. Weaknesses in a third party security can be exploited to get access to the network or data of financial firms. At TechMagic, we integrate a variety of modern solutions, making sure that all the implemented safeguards work properly and nothing endangers the system.
AI-related cyber threats
Artificial intelligence enriches the banking sector with notable advancements in fraud monitoring, risk management, and customer support. At the same time, AI-related technologies create the ground for new security threats. AI is empowered to develop synthetic media, such as realistic fake videos or audio, known also as deepfakes. Cyber attackers implement deepfakes to pretend to be bank representatives in social engineering attacks and approach your personal details and information.
Remote workforce
Remote work has become the norm in many spheres of activity, including the banking sector. Still, when a remote worker has access to important or sensitive information, there are additional risks associated with data breaches. Remote work creates potential cyber threats as unsecured networks, weak endpoint security, and physical security concerns.
Distributed denial of service
A DDoS attack is a cyberattack that overloads a system with traffic. This prevents legitimate users from accessing their accounts, making transactions, and contacting customer support.
Data breaches
Unencrypted data stored in a device of a bank is the root of many potential threats. If your data is unencrypted, in case of a breach hackers can easily access all the sensitive data and use it against you and your customers.
Let’s explore real cases: Top cybersecurity attacks on financial institutions
Digital transformation has restructured the way we manage our finances. Online banking and mobile payment apps provide users with convenience, but they also set the basis for new vulnerabilities to arise in financial systems. In 2022, 800,944 cyber crimes were reported in the USA.
Cybercriminals are continuously inventing sophisticated formulas and approaches to make use of these weak points and attack financial institutions and their customers. Let’s have a look at recent cyber attacks on financial institutions to get a wider perspective on the complex strategies used by attackers and the destructive consequences they may result in.
$13.7 million OCBC phishing scam

On December 23, a phishing scam targeting the Singaporean bank OCBC resulted in a loss of 13.7 million U. S. dollars. Approximately 790 banking customers fell victim to the incident. Affected persons received untruthful messages claiming that there were issues with their banking accounts, asking them to click on a link to solve the problem.
After clicking, victims were redirected to fake bank websites and demanded to type in their account login information. As soon as they clicked on the phishing link, attackers got an opportunity to log in to the bank account of a victim and withdraw all funds from it. Affected people would realize they had been scammed once they got messages from a legitimate bank notifying them of unauthorized transactions charged to their bank accounts.
885 million files First American Financial Corp. data breach

On May 24, First American Financial Corporation faced a data breach involving up to 885 million financial and personal records linked to real estate operations. The documents, dated back to 2003, were exposed as a result of a common website design error. The breached data included bank account information, mortgage and tax records, driver licenses images, social security numbers, and other sensitive information.
A web page link giving access to sensitive data was not secured by a multi-factor authentication policy. Anyone with access to at least one document link could approach others by changing the figures of a record number. The company shut down the website, but a lot of the pages were still accessible on the archive websites. Such personal details as names, email addresses, agents and buyers mobile phone numbers were compromised. With this information, it is possible to commit such cyber crimes as identity theft, malware injections, and ransomware attacks.
$615 million Ronin cryptocurrency theft
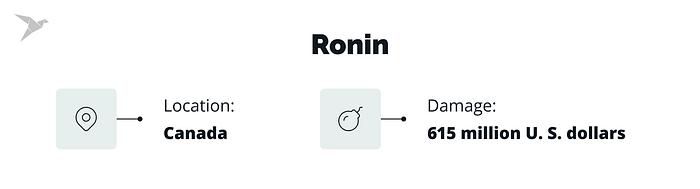
On March 23, blockchain project Ronin lost 615 million U. S. dollars due to a cyber attack. Cyber attackers exploited a function enabling users to transfer their digital assets from one crypto network to another one. It is thought to be the second-largest cryptocurrency theft. Ronin mentioned that the hacker had used stolen private passwords required to access crypto funds to get hold of them. The United States assigned the cyber attack to the North Korean state-backed hacking collective Lazarus Group and imposed new sanctions against them.
Risk Awareness
Customer information disclosure can lead to harmful consequences, such as:
- Identity theft
- Scam transactions
- Account draining
- Unauthorized charges issues
- Fraudulent money transfers
These deceitful activities not only result in direct financial expenses for the bank but also require costs for investigations, remediation, and compensation to customers. In addition to instant financial losses, banking institutions must deal with regulatory and compliance penalties for non-adherence to policies to keep customer data safe.
Despite the financial harm, the reputational damage after a cyber attack usually appears to be catastrophic. Customer trust can be broken after the incident. Recovering trust necessitates time, resources, and serious marketing strategic actions.
The effect on customers can be no less destructive. A data leak results in significant financial losses for individuals. Accounts opened in their name can leave them saddled with debt, while unauthorized transactions can drain their savings.
The evolving nature of cyber threats further intensifies the challenge. Hackers are constantly innovating and developing new methods to exploit vulnerabilities in security systems. Phishing emails become more sophisticated, malware disguises itself better, and social engineering tactics become more convincing. This constant evolution necessitates a proactive approach from banks.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Efficient Protection
Advanced security solutions help banks to succeed in maintaining a robust security system. Let’s have a look at the key ones.
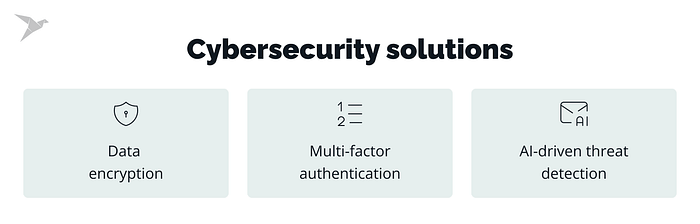
Data encryption
Data encryption encodes sensitive information such as personal profile details or social security numbers. This process makes the data unusable for anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key. Encryption minimizes the damage caused by such attacks and builds customer confidence by prioritizing data security.
Multi-factor authentication
MFA serves as an additional security measure for online and mobile banking. Beyond just a password, MFA necessitates another confirmation step, such as a code received on your phone or a fingerprint scan. This notably impedes unauthorized access, even if hackers manage to steal your password. With MFA, it becomes considerably more difficult for criminals to pretend to be you and gain access to your financial information.
AI-driven threat detection
AI-driven threat detection systems meticulously analyze massive datasets to identify unusual activity in real-time. AI can detect and respond to cyberattacks with greater speed and efficiency as it recognizes patterns and inconsistencies that might elude traditional methods. This empowers banks to prevent potential breaches before they occur.
Regulatory Compliance
A system of regulations has been established to safeguard consumers and decrease security weaknesses in the banking system. Financial organizations must be aware of these crucial requirements to act legally and in a secure way.
Adhering to cybersecurity regulations and standards is not only about avoiding penalties. It proves the loyalty of a bank to protect customer data and maintain a secure environment. Strong cybersecurity practices build trust with both customers and regulators, which results in a more secure and stable financial system.
These standards often manage data security safeguards, risk assessments, robust protocols for customer data privacy and protection, as well as constant system monitoring and incident reporting.
Government regulations
On a global scale, governments take action by enacting laws that require banks to implement specific cybersecurity practices. These regulations can dictate various aspects of data security, including what needs to be protected, how to handle breaches, and how personally identifiable information privacy is safeguarded. Examples include the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union.
